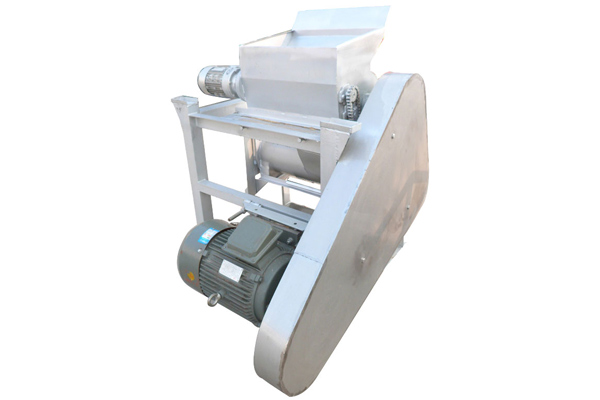
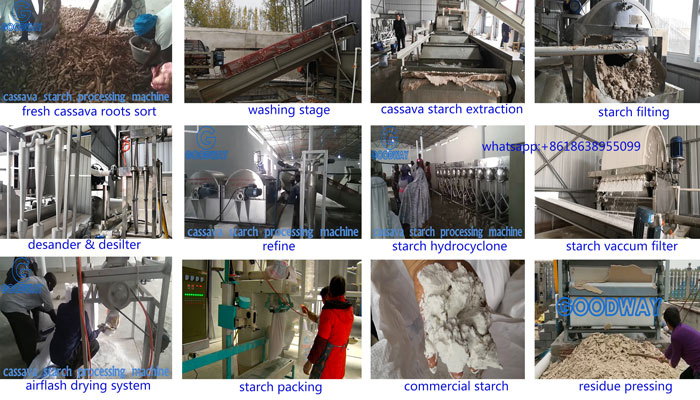
The cassava starch production process is roughly as follows:
Fresh Cassava-Washing -Starch Extraction-sifting-concentration-starch drying as below.
It can be known from the production process of tapioca starch that most of the waste water is formed during the process of cleaning raw materials, pulp residue screening, starch extraction and other processes.
In the first two steps, it is necessary to clean the sediment and root epidermis of cassava. The remaining impurities will affect the quality of the extracted starch. After washing, the waste water contains a lot of sediment and cassava skin, SS (suspended solids) content is at a high level, and the content of pollutants is greatly reduced after precipitation.

In the extraction stage of tapioca starch, wastewater from traditional production is used, and the supernatant after precipitation contains water-soluble starch, protein, polysaccharides, amino acids, and several inorganic salts. There are many nutrients containing nitrogen and phosphorus, good biochemical properties, no toxic substances and heavy metals, and the value of recyclable resources is very high. Due to different quality of sweet potatoes and different processing methods and time, the COD of the cassava starch wastewater of each batch is not the same. PH value is about 4.0-4.5, COD is about 10000mg/L, SS is about 3000mg/L.

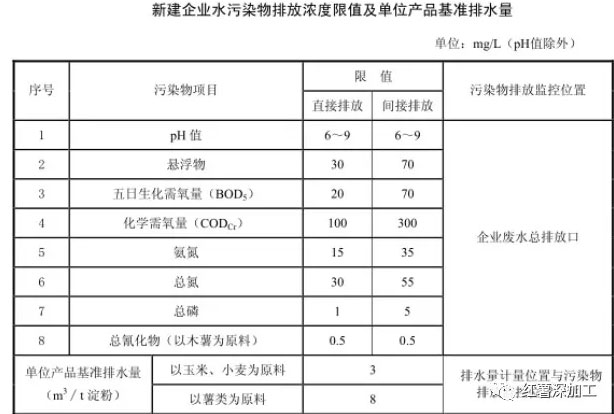
The previous cassava starch processing process consumes a lot of water resources, the starch extraction rate is low, and the wastewater contains more pollutant components. If it is discharged into nature without purification, it will seriously affect the surface water quality in local areas. In 2010, the relevant government departments adjusted the starch wastewater discharge standards, the specific requirements are shown in the table below:
The wastewater formed in the backward cassava starch production process needs to be purified, and at the same time, the related processes and cassava starch processing equipment should be improved. At present, the automatic cassava starch production line adopts multi-stage cleaning in the cleaning stage. The screw conveyor type dry cleaning machine is used to roll forward without water to remove the surface sediment and save energy and water. Combined with other washing machines, the raw materials can be fully cleaned, while saving energy and water. When crushing and extracting starch, modern cassava starch processing equipment adopts two-stage crushing, multiple panning, squeezing and filtering, and counter-current circulation of water, which can not only increase the starch extraction rate, but also reduce water consumption, thereby reducing waste water.
Of course, no matter whether it is traditional cassava starch processing or modern cassava starch processing equipment, starch processing is to produce wastewater, which must be treated before being discharged. However, the amount of waste water in the fully automatic cassava starch processing equipment is less, and it is also easier to collect and process.
Remarks: COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) is the chemical oxygen demand. It is a chemical method to measure the amount of reducing substances that need to be oxidized in the water sample. It can roughly represent the amount of organic matter in sewage. COD is an important indicator of organic pollution in water bodies, which can reflect the degree of water pollution. In the study of river pollution and the nature of industrial wastewater, as well as the operation and management of wastewater treatment plants, it is an important and fast-determining organic pollution parameter.

 EN
EN
 fr
fr  es
es  it
it  pt
pt 











